DIY Vertical Garden Ideas: Innovative Ways to Green Your Space
Vertical gardening is an innovative way to bring greenery into your home, regardless of your living space size.
You can creatively utilize vertical surfaces to cultivate flowers, succulents, edible herbs, and other plants.
This method adds a unique aesthetic to your home and maximizes your gardening area. This is especially beneficial if you have limited ground space.
As urban living becomes more compact, vertical gardens offer a clever solution for growing your own green oasis.

When considering a do-it-yourself vertical garden, there are numerous design ideas to choose from. Each design has its own set of requirements and benefits.
You can repurpose old furniture or use modular planting systems and hanging planters. Some vertical gardens are soil-based, while others use hydroponic systems, a soil-less gardening method.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener looking for a new challenge or a beginner eager to add some plant life to your environment, starting a vertical garden can be a satisfying project.
Selecting the right plants is crucial for the success of your vertical garden.

You should consider the light conditions, the climate of your area, and the amount of care the plants will need.
Hardy and low-maintenance varieties tend to do well, as they can thrive even with minimal intervention.
Regardless of your choice, the key is creating a living wall that flourishes, bringing beauty and a touch of nature into your vertical spaces.
Table of Contents
Understanding Vertical Gardening

Vertical gardening is an innovative method that allows you to grow plants upward on various structures. This approach can be particularly useful for making the most of limited space.
Benefits of Vertical Gardens
- Space Efficiency: Growing upwards maximizes your gardening area, which is ideal for small gardens or balconies.
- Accessibility: Vertical gardens are easier on your back and knees because they reduce the need for bending or kneeling.
- Microclimate Control: Vertical gardens can regulate temperature and air flow by creating shaded regions and wind barriers.
- Aesthetics: A well-designed vertical garden can transform an empty wall into a living piece of art.

Essential Elements for Vertical Gardening
- Structural Support: Durable supports such as trellises, wall planters, or modular systems are crucial.
- Growing Medium: Consider lightweight options like potting mix, coco coir, or felt pockets that are well-draining.
- Irrigation: An efficient watering system, possibly drip irrigation or a self-watering mechanism, is key for even moisture.
- Plant Selection: Choose plants that suit vertical growth, such as ferns, succulents, or certain edibles like strawberries.
Selecting Suitable Locations

When setting up a vertical garden, picking the right location is crucial for plant health and ease of maintenance. Your choice will affect how well your plants grow.
Assessing Space and Light
Before installing a vertical garden, evaluate the space’s dimensions and the daily light it receives.
Ideal light conditions vary depending on what you plan to grow:
- Full Sun: 6+ hours of direct sunlight (e.g., most vegetables, sun-loving flowers)
- Partial Shade: 3-6 hours of direct sunlight (e.g., many herbs, some perennials)
- Full Shade: Less than 3 hours of direct sunlight (e.g., ferns, certain foliage plants)
Note the direction windows face if indoors or the sun’s path if outdoors. Measure wall space to ensure your garden will fit without obstructing paths.

Outdoor Versus Indoor Considerations
Outdoor and indoor environments offer different advantages and challenges for vertical gardens:
- Outdoor:
- Pros: More space, natural light, rainwater access
- Cons: Exposure to weather, pests
- Indoor:
- Pros: Climate control, fewer pests
- Cons: Limited space, need for artificial lighting or specific window placement
Ensure outdoor walls can withstand elements and support weight. Consider the proximity to natural light sources and any necessary structural support. Use a waterproof backing to prevent moisture damage to walls.
Designing Your Vertical Garden
In designing your vertical garden, it’s imperative to determine the proper structure and consider aesthetics to create a visually pleasing arrangement.
Choosing a Structure
For your vertical garden, choose a structure based on space availability, light exposure, and plant selection. Consider the following options:
- Freestanding Walls: Ideal to move your garden for varying light conditions.
- Wall-Mounted Frames: Use these to create a permanent display on an existing wall.
- Stacked Planters: A great space-saver, perfect for balconies or small patios.
- Recycled Materials: Pallets, crates, and old frames can be repurposed for an eco-friendly choice.

Aesthetics and Arrangement
Your garden’s visual appeal greatly depends on how you arrange the plants. Various factors affect aesthetics:
- Plant Color: Group plants with complementing colors or create a monochromatic scheme.
- Plant Texture and Size: Mix and match leaf textures and plant sizes for depth and interest.
- Symmetry vs. Asymmetry: Decide whether a symmetrical design or an asymmetrical, organic arrangement suits your space better.
Remember to consider each plant’s growth habit and needs to ensure your vertical garden is not only beautiful but also thrives.
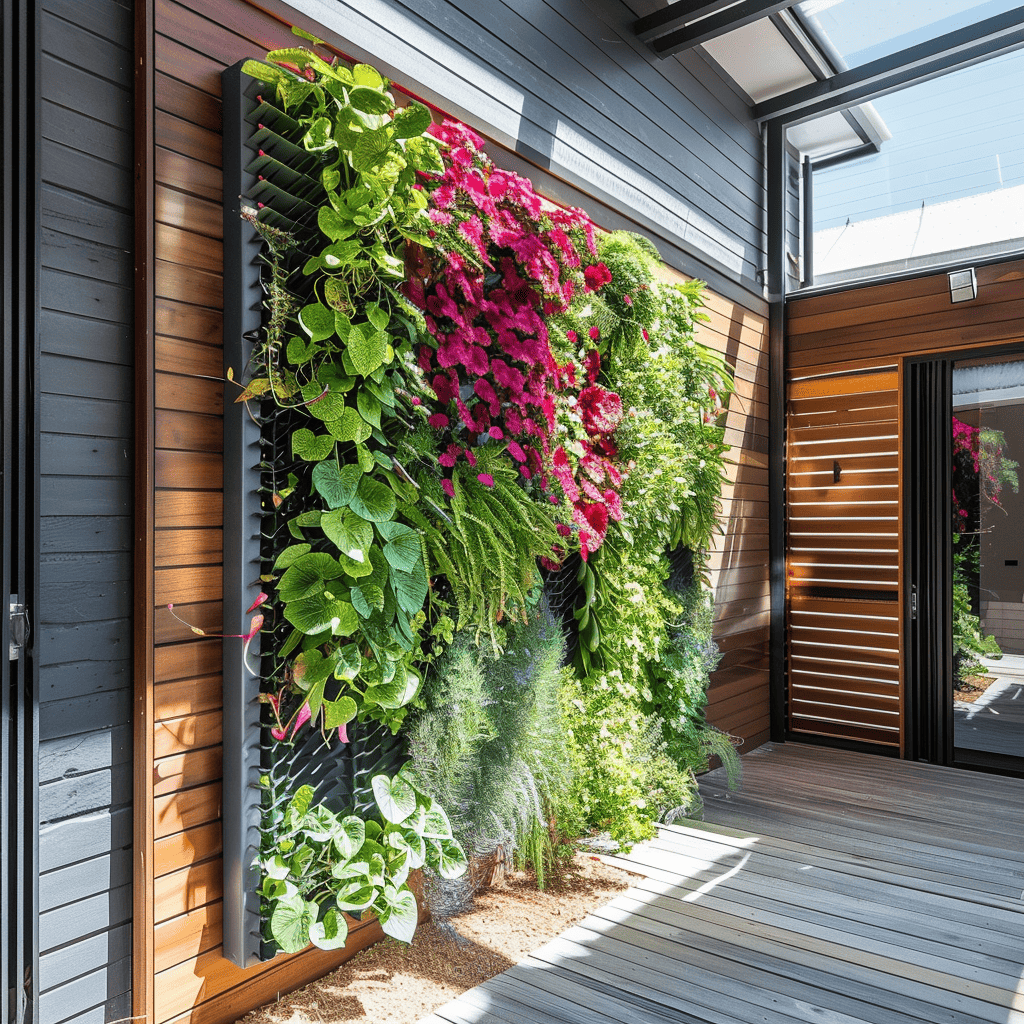
Choosing Plants for Your Vertical Garden
Selecting the right plants is critical for a thriving vertical garden. You’ll want species that naturally grow upwards and require similar care conditions.
Best Plants for Vertical Growing
When selecting plants for your vertical garden, choose varieties with a climbing or trailing growth habit. Here are some top choices:
- Succulents: Ideal for their low maintenance and shallow root systems. Examples include:
- Echeveria
- Sedum morganianum (Burro’s Tail)
- Ferns: Great for their lush foliage and adaptability to vertical growing. Notable ferns are:
- Adiantum (Maidenhair Fern)
- Nephrolepis exaltata (Boston Fern)
- Vining Plants: Offer a cascading effect. Choose from:
- Hedera helix (English Ivy)
- Epipremnum aureum (Devil’s Ivy)
- Herbs: Perfect for edible vertical gardens. Recommended herbs:
- Thymus vulgaris (Thyme)
- Mentha (Mint)
Plant Care and Growth Requirements
Understanding your chosen plants’ care and growth requirements will ensure they flourish.
- Light: Most vertical garden plants need bright, indirect light.
- Succulents: Require at least six hours of sunlight a day.
- Ferns and Herbs: Prefer shadier spots.
- Watering: Consistent moisture levels are key, but be cautious of overwatering.
- Succulents: Allow soil to dry out between watering.
- Ferns and Vining Plants: Need moist, well-drained soil.
- Soil: A quality, well-draining potting mix is crucial.
- All plant types: Use soil that provides ample aeration and prevents root rot.
- Feeding: Nutrient-rich fertilizers support growth.
- Herbs and Vining Plants: Benefit from regular feeding during growing seasons.
- Succulents: Require less frequent fertilization.
Each plant has unique needs, so always research the specific varieties you choose to include in your vertical garden for optimal growth conditions.
DIY Vertical Garden Projects
Vertical gardens are an innovative way to bring greenery into your home without taking up valuable floor space. These projects can transform a bare wall or fence into a lush and productive space.
Recycled Materials Garden
Using recycled materials for your vertical garden saves money and contributes to environmental sustainability.
Gather old plastic bottles, shoe organizers, or tin cans. Clean, paint, and mount them on a wall or fence.
Ensure drainage holes are added so that excess water can escape. Label each planter with the plant’s name using weather-resistant tags for a neat and organized appearance.
Pallet Garden Project
Pallets provide a sturdy and rustic frame for a vertical garden.
To start, secure a pallet against a wall or fence—ensure stability to prevent accidents.
Before planting, line the pallet with landscape fabric to create pockets that will hold the soil and plants in place.
Choose plants that are suitable for vertical growth, such as herbs, succulents, or small flowers.
Wall-Mounted Planters
Investing in wall-mounted planters creates a modern and clean look for your vertical garden.
These can be purchased or handmade from wood, metal, or ceramic.
When installing, space the planters evenly and firmly fix them to the wall.
Consider using a variety of plants for textural contrast and visual interest.
Remember to water regularly, as wall-mounted planters may dry out faster than ground-level gardens.
Irrigation Solutions

Proper watering is crucial for the health of your vertical garden.
Self-watering systems and drip irrigation setups are two efficient methods for ensuring your plants receive the right amount of water.
Self-Watering Systems
Self-watering systems are an excellent way to maintain moisture levels with minimal oversight.
These systems typically consist of a reservoir that holds water and a wicking mechanism that draws water into the soil as needed.
- Reservoir Types:
- Bottles: Use recycled water bottles for smaller setups.
- Tanks: Larger gardens may need a tank for increased capacity.
- Wicking Material: Cotton ropes or felt strips are effective options.
Drip Irrigation Setups
Drip irrigation setups offer a precise watering solution that saves time and conserves water.
This method gently delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubing.
- Components:
- Tubing: The main hose connected to a water source.
- Emitters: Devices that release water slowly at each plant site.
- Timers: Optional, for automatic scheduling.
- Installation Tips:
- Ensure the system is pressure-regulated for even water distribution.
- Regularly check emitters to avoid clogs and ensure proper flow.
Maintenance and Care
A thriving vertical garden requires regular maintenance and care.
Focus on the pruning and harvesting techniques specific to your plants, and proactively manage pests and diseases to ensure longevity and health.
Pruning and Harvesting
- Pruning: Regularly inspect your plants for dead or overgrown foliage. Use sharp, clean scissors or pruning shears to make clean cuts.
- Harvesting: Pick ripe fruits or vegetables early in the day for peak freshness. Herbs should be harvested before they flower for best flavor.
Pest Management and Disease Prevention
- Pest Management:
- Inspect plants weekly for signs of pests.
- Introduce beneficial insects such as ladybugs for natural pest control.
- Utilize insecticidal soaps or neem oil as non-toxic options for infestations.
- Disease Prevention:
- Ensure proper air circulation around plants.
- Water at the base and avoid overhead watering to keep foliage dry.
- Remove and dispose of any diseased plant material promptly to prevent spread.
Innovative Vertical Gardening Techniques
Vertical gardening can transform your space into a lush, green haven while saving you ground area.
These techniques rely on advanced systems to maximize plant health and growth.
Hydroponic Vertical Systems
Hydroponic systems let you grow plants without soil, nourishing them directly through nutrient-rich water solutions.
Key components of a hydroponic vertical garden include:
- Support Structure: A sturdy frame to hold plant containers.
- Plant Holders: Net pots or similar containers for root support.
- Reservoir: To hold the nutritional solution.
- Pump and Irrigation: To circulate the solution from the reservoir to the plants.
- Lighting: Artificial lights if natural light is insufficient.
Setup Steps involve:
- Assemble the frame and attach plant holders.
- Connect the pump and irrigation system.
- Fill the reservoir with nutrient solution.
- Insert plants into holders and begin the growing cycle.
Aquaponic Approaches
Aquaponics combines hydroponics with fish farming. Fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and plants clean the water for fish.
Essential Components:
- Fish Tank: A tank for raising fish.
- Grow Beds: Where the plants will grow.
- Water Pump and Filter: To move and purify water between the fish tank and grow beds.
- Plants and Fish: Compatible species that will thrive together.
Basic Steps:
- Set up the fish tank and grow beds in close proximity.
- Install the pump and filter to connect the two systems.
- Add fish and plants to the grow beds in the tank.
- Maintain the balance between fish and plant life for a successful system.





